Summary
In an era where cyber threats evolve daily, traditional security models fall short. The concept of AI in Zero Trust Security offers a powerful solution: never trust by default, always verify. This blog explores how integrating AI transforms zero trust from rigid rules into dynamic, adaptive defense. From real-time anomaly detection and adaptive authentication to automated incident response and continuous learning, AI enables systems to withstand sophisticated attacks like deepfakes and GenAI-powered phishing. With real-world use cases across finance, healthcare, retail, and government, the article shows not only why AI is essential in zero trust, but how to implement it step-by-step.
AI in Zero Trust Security: smarter, intelligent, and more proactive security systems.
Ongoing investment, innovation, vulnerabilities, threats, and more demand for a proactive, mindful, and quick-on-trigger security that serves in real-time. Gone are the days of rigid, boxed rules with predefined boundaries. With highly manipulative intruders around, it’s time to weaponize with AI. A more advanced and full-scaled frontline hero to work on every microsegment, ensuring better protection and seamless user experience.
But is it the right approach? How should an enterprise adapt it? And how is AI in Zero trust cybersecurity resilient?
We got all your queries covered. However, to understand this further, let’s take a quick look at zero-trust security.
Whether you’re in fintech, healthcare, or edtech, an AI development company helps you navigate complexities, spot risks, and build smart solutions to stand out in a crowded market.
What is Zero Trust Security?
“Trust only what you see” is not limited nowadays to life, but also applies to cybersecurity. With thousands of manipulative tools, the increased adoption of AI, and deepfake strategies, multiple novel security threats are demanding a zero-trust security architecture that is stronger and more resilient.
Zero-trust security means that nothing is trusted by default; trust must be earned every time. It’s beyond perimeter-based security, helping to evolve and build a stronger security posture.
Zero trust is a methodology, not a fancy tool or ready-to-purchase product. It is a model that requires a shift in approach, based on a set of rules and traditional methods.
Consider it as such – You are the king of the castle. This castle is safe from predators. Assuming that everyone inside the castle is a supporter.
The limit of breach is not limited to outsiders; even sophisticated hackers or ‘sleeper cells’ are within the premises, ready to be activated anytime and anywhere. This calls for zero-trust security, which is based on the principle of ‘Never trust, always verify’.
This is where zero-trust security enters. Once an attacker manages to breach the perimeter with effective strategies, gaining a position or staying within your ‘castle’ becomes impossible. Zero trust security creates multiple checkpoints (layers) for everyone entering. Whether an employee, an outsider, or someone from the same family, no one can inherently gain trust; they must undergo verification each time.
Companies often lack centralized data. It’s fragmented and scattered across cloud vendors, remote teams, accessible points from multiple devices, etc. This makes it difficult to manage security at a single point for the entire network. Even though two-way or multi-layer authentication might fall into the fallacies. This calls for Artificial Intelligence in Zero trust security to outgrow with a stringent, more resilient, and robust security posture.
Zero trust has long been the foundation of cybersecurity. However, with the growing threat of AI-powered attacks, increasing vulnerabilities, and escalating issues, the demand for AI to counter AI is becoming increasingly necessitated.
Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword
AI is empowering for defenders, but it’s also giving rise to cyberattacks with GenAI and deepfakes. Attackers are exploiting AI capabilities to make phishing more targeted and realistic. With data from social media, AI/ML-trained models can mimic writing styles, and as more attackers craft personalized and authentic mimicked messages, anyone can fall prey.
Additionally, with the aid of AI, attackers can identify the weak spot to gain entry and exploit vulnerabilities. They develop an adaptive AI-powered malware that can change and adapt as the system works. If blocked from one window, it quickly changes its direction to intrude from other windows.
Overall, this makes automation attacks faster and more efficient. Hackers no longer need to use manual maths or try trial-and-error methods to launch more attacks. This underscores that those who are weak in security or still follow rule-based models are the prime victims.
With the principles of Artificial Intelligence in zero trust, a robust framework is required for today’s security strategies.
Fortunately, the AI and ML capabilities are also high on the defender’s side. Artificial Intelligence in Zero Trust security can meet every checkpoint and beyond it. Threat detection, vulnerability management, incident response and threat hunting, and reducing the security operations center. It’s an answer to holistic security coverage – from detection to remediation.

Traditional Security vs. AI in Zero Trust Security: Areas of Impact
The evolution of threats is expanding. With its complexity and dynamicity, the zero-trust model presents an effective approach to neutralizing these threats. The fundamental principle of assuming no implicit and verifying everything promotes a proactive and innovative approach to security in an organization.
Here is a glimpse into how, with an evolving environment, you need a forward-thinking approach to AI in zero-trust cybersecurity for your organization.
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | Zero Trust Approach | AI in Zero Trust Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability Detection | Relies on static, predefined rules and periodic scans, often missing new vulnerabilities. | Continuous monitoring and verification of all devices/users, reducing vulnerability gaps. | AI-powered UEBA and predictive analytics detect anomalies and predict zero-day vulnerabilities in real-time. |
| Breach Prevention | Perimeter-based security assumes internal safety, leaving insider threats unchecked. | No implicit trust; enforces strict access controls and segmentation to limit breaches. | AI enhances IAM with behavioral biometrics and adaptive authentication, instantly blocking suspicious activities. |
| Response to Breaches | Manual or semi-automated responses result in slower mitigation and increased damage. | Automated responses with predefined policies, faster containment of breaches. | AI automates device isolation, prioritizes threats, and learns from incidents to strengthen future defenses. |
| Adaptability to Threats | Limited adaptability; struggles with sophisticated AI-driven attacks like deepfakes. | Dynamic policies adjust to context, but may lack real-time threat intelligence. | AI models trained on attack patterns can adapt to evolving threats, such as GenAI-powered phishing or adaptive malware. |
| Cost of Breaches | High costs are associated with prolonged detection and response times, resulting in an average of approximately $4.35 million per breach. | Reduces costs by limiting breach impact (e.g., saves approximately $1.76M with a mature zero-trust solution). | Further reduces costs through faster detection, automated response, and predictive prevention. |
Security Lag – Enterprises Not Leveraging AI in Zero Trust Cybersecurity
Pathology labs, tech titans, healthcare companies, and pharmaceutical companies are the primary targets of attackers and hackers. They get an enormous amount of data, birthdates, credentials, and much more. Well, the situation is alarming. Attention-grabbing headlines related to data security are on the rise. Performing a check ip address location regularly can help identify suspicious access points and enhance security protocols.

This is a stark reminder of vulnerabilities lurking within our network. 63% of companies have already adopted zero-trust security; still, most of them are hopping around.
The obsolete are weak and the first victims to be preyed upon. Traditional security systems, often trained on historical data or legacy methods, struggle to counter sophisticated attacks, such as zero-day exploits or advanced persistent threats. To stay ahead, businesses must adopt innovative, multi-layered security frameworks that are difficult for AI-powered attacks to bypass.
Insights of Targeted Victims and the Costs They Paid
In 2021, the global average cost of a data breach was $2.4 million, with healthcare being the most affected sector, at $9.23 million per breach. This breach compromised credentials, which cost an average of $4.77 million to resolve, and took 250 days to detect.
For AT&T, a Snowflake cloud misconfiguration exposed call and text data of a million customers, which translates to $50 million in response efforts. Additionally, an extra $10 million is added, along with fines. In the same year, their share prices dropped by 3%.
In 2017, a failure to patch exposed 147 million people, resulting in a $1.4 billion settlement, fines, and upgrades for Equifax. These breaches were detected after 76 days and caused long-term reputational harm.
These are some examples; there are millions of enterprises that are unaware of these fallacies and are victims. However, this can be avoided by building a better and stronger next-generation cloud security system.

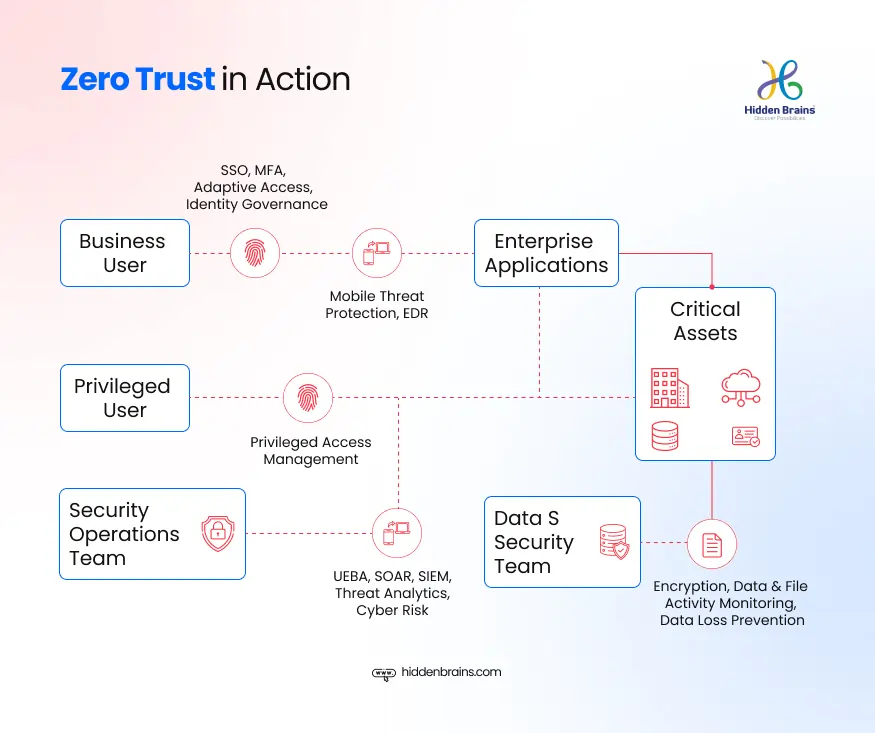
How Zero Trust Principles Work with AI Integration?
The Zero Trust security model operates within the framework of ‘Never trust, always verify,’ which translates to never implicitly granting anyone access without proper validation. By integrating AI and ML, the zero-trust cybersecurity system evolves into a more dynamic, predictive, and adaptive one that counters sophisticated cyber threats. Leveraging the power of AI and ML tools to analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and automate responses, Artificial Intelligence in zero-trust environments becomes an indispensable tool for enterprises.
Explore the intricacies of Zero Trust principles and how AI leverages them.
Verify Explicitly
No assumptions and predictions. AI in Zero trust security verifies every device, user, or application, whether it’s inside or outside organizations. Every access is authenticated and authorized using a strong identity verification method, such as MFA (multifactor authentication).
- Example – A user logging in from an unfamiliar location must provide additional verification, such as a one-time code, even if their credentials are correct.
- Outputs – This eliminates implicit trust based on network location, ensuring every interaction is safeguarded.
- AI in Zero Trust Security: AI enhances verification by analyzing user behavior, device attributes, and contextual data in real time. It identifies anomalies, such as logins from unusual locations, and triggers additional authentication steps, efficiently and accurately reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Use Least Privilege Access
User, devices, and applications should have limited or specific access to resources. It’s not open to everyone; it’s for specific tasks and only for the duration required. This principle is implemented through role-based access control or just-in-time access. This approach minimizes the attack surface by limiting access to credentials in the event of a compromise.
- Example – An authoritative person has temporary access to a limited database but cannot access other sensitive systems or data.
- Outputs – Restricting permission secures the data from potential damage, and compromised accounts or lateral movements are reduced.
- AI in Zero Trust Role: An AI-enabled security framework, whether inside or outside the network, ensures that users’ applications or systems are granted only the minimum permissions necessary to perform specific tasks, thereby reducing the attack surface and mitigating risk to the overall structure. Embedding the least privileged access to every layer of access control reduces the risk and creates a robust, adaptive security posture.
Assume Breach
Assuming the worst-case scenario, the breach has already occurred or can happen at any time. This calls for proactive measures, such as network segmentation, encryption of data, and rapid incident response protocols. It minimizes the blast radius of a breach through the use of isolation and containment strategies.
- Example – Micro-segmentation and fragmentation ensure that if the attacker gains access to a part of a network, they cannot easily move to other parts.
- Outcome – This approach transitions from a prevention-only model to a resilient one that limits damage and enables faster recovery.
- AI in Zero Trust Security: AI supports breach containment by detecting suspicious activity through real-time analytics, isolating affected systems, and enabling rapid response. It reduces the chances of a complete breach and accelerates recovery, thereby maintaining overall system resilience.
Device Security
The health of every device matters and should be validated for security compliance. Uncompromised or non-compliant devices, those lacking an antivirus system or those that are unpatched, should be strictly denied or quarantined.
- Example – A company uses an endpoint management solution that restricts access from devices with outdated operating systems.
- Output – Unsecured devices are gateways for hackers and attackers; continuous and healthy systems prevent weak links.
- AI in Zero Trust: AI continuously assesses device health, identifying risks like missing patches or malware. It automates enforcement actions, such as isolating non-compliant devices, ensuring only secure devices access the network, and reducing the risk of exploitation.
Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Don’t linearly trust. Evaluate and reevaluate constantly. This involves real-time monitoring of user and system behavior, analyzing logs, and using analytics to detect anomalies that could become potential threats. Tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) or User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) are used to support this.
- Example – Anomalies, such as the sudden download of a large amount of data at an unusual time, may cause the system to consider it a red flag or suspicious activity and trigger further authentication or block access.
- Output – Frequent monitoring ensures that even if an attacker gains access, their actions can be halted or denied before in-depth harm occurs.
Security for All Communication
AI in cybersecurity leaves no space for extraterrestrial activity. All data transmission, whether from an organization or an external system, is encrypted and secured using protocols such as TLS or VPNs. This keeps data unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Example – An employee accessing a cloud application at the airport or a Wi-Fi network uses an encrypted connection to prevent eavesdropping. Using a Windows VPN can provide an added layer of security, ensuring that data transmitted over public networks remains protected.
- Output – Securing communication channels prevents data leaks or man-in-the-middle attacks.
- AI in Zero Trust Security: AI analyzes vast amounts of data in real time, identifying anomalies and potential threats with high accuracy. It enables rapid detection and response to suspicious activities, minimizing the window for attackers to operate and enhancing security posture.
An Insightful Read – Generative AI vs. Agentic AI – Which One Lead in 2025?
Policy Driven Automation
The Zero Trust model relies on automated regulations to efficiently and widely oversee security decisions. These guidelines, typically directed by instruments such as Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems or Software-Defined Perimeters (SDP), determine how validation, authorization, and accessibility are permitted, taking into account current situations.
- Example – A policy automatically revokes access to a user whose device fails a security check, without any manual intervention.
- Output – AI in Cybersecurity through automation reduces manual errors, speeds up response time, and ensures consistent application of security controls throughout complex environments.
- AI in Zero Trust Security Benefits: AI monitors communication channels for vulnerabilities or suspicious patterns, ensuring encryption protocols are consistently applied. It detects attempts to intercept data and strengthens defenses, safeguarding sensitive information during transmission.
Data-centric Security
AI relies on data for training, inference, and decision making. AI in zero-trust cybersecurity protects data, no matter where it resides or how it is accessed, rather than solely relying on securing the perimeter, network, or devices. Zero trust ensures strict controls, encryption, and monitoring to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, even in dynamic and distributed environments.
- Example – Sensitive customer data may be accessible only to specific roles and trusted devices, with all actions logged.
- Outputs – Data is a primary target of cyberattacks, and focusing on it ensures that even if the other counterparts fail, the critical asset remains secure.
- AI in Zero Trust Delivers Benefits: AI scans data security by categorizing sensitive data, tracking access patterns, and identifying unauthorized attempts to access or exfiltrate data. AI safeguards valuable assets, keeping trust intact in dynamic and distributed environments.
A quick glimpse that helps you evaluate how AI in Zero Trust cybersecurity adds value in each area.
| Feature | Traditional Zero Trust | AI-Powered Zero Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Predefined rules | Adaptive, behavior-based |
| Authentication | One-time login | Continuous, contextual |
| Threat Detection | Manual/signature-based | Real-time, AI anomaly-based |
| Incident Response | Manual | Automated, machine learning |
| Micro-Segmentation | Static | Dynamic, AI-driven |
| Threat Intelligence | Historical data | Predictive analytics |
How AI Works in Zero Trust Security?
AI enhances Zero Trust by analyzing vast datasets, detecting patterns, and automating responses across multiple security layers. Here’s a breakdown of its core mechanisms:
Real-Time Anomaly Detection and Predictive Analytics
- Mechanism: AI-powered tools, such as User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), monitor network traffic, user activities, and device logs in real-time. ML algorithms establish baseline behaviors and flag anomalies, such as unusual login patterns or unexpected data access. Predictive analytics uses historical and current data to forecast potential zero-day exploits.
- Example: AI analyzes endpoint behavior to detect vulnerabilities, such as misconfigured devices or unpatched software, before attackers can exploit them.
Adaptive Authentication and Access Control
- Mechanism: AI enhances Identity and Access Management (IAM) by dynamically assessing risk factors, including user location, device health, and behavioral biometrics. It enforces adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and least-privileged access, ensuring only verified entities gain entry. AI integrated with Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) creates microsegmented networks, limiting lateral movement.
- Example: Adaptive multi-factor authentication uses AI to evaluate login contexts, requiring additional verification for high-risk attempts, such as logins from unfamiliar locations.
Automated Incident Response and Remediation
- Mechanism: AI automates threat response by analyzing attack vectors, isolating compromised endpoints, and executing predefined playbooks. It prioritizes incidents based on severity and learns from each event to refine future responses, reducing attacker dwell time. AI-driven Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response platforms streamline workflows in Security Operations Centers (SOCs).
- Example: A custom AI security solution to isolate breached devices and revoke access, mitigating incidents in minutes and minimizing damage.
Continuous Learning for Threat Adaptability
- Mechanism: AI models continuously train on global threat intelligence, historical attack data, and real-time events to identify emerging patterns, such as GenAI-powered phishing or adaptive malware. This enables proactive policy adjustments and predictive defense against sophisticated attacks, such as deepfakes or ransomware.
- Example: Leveraging AI to correlate threat intelligence, adapting to new attack vectors like AI-crafted phishing emails that mimic legitimate communication.
AI for zero trust security. It’s about ditching the traditional model and adapting to a new one in response to the demand and dynamism of the ecosystem. Evolution is beneficial, and with time, it is inevitable. Even national and state authorities have been advised to adopt zero-security AI in governance and defend proactively instead of reactively.
Zero Trust In Action – Use Cases
Zero-trust security has never been apparent. With more advanced and sophisticated users across various industries, there is a growing need for agencies to adopt zero-trust security as their mainstream approach to security. Enforcing verification, least privilege, and granular access controls, Zero trust meets the organization’s concerns and brings practical application in action.
Financial Services – Secure Banking
Banking and financial institutions process massive data daily, handling over 1.9 billion transactions monthly. This makes them prime targets for cyberattacks, such as phishing and account takeovers. Zero Trust security establishes multiple layers of protocols, including continuous authentication and least-privileged access, making unauthorized access to financial records nearly impossible and thereby limiting fraud and data breaches.
- Zero Trust Approach: Enforces multi-factor authentication (MFA) for every user and device, segments payment systems, and restricts access to sensitive data based on roles.
- AI Enhancement: AI analyzes vast datasets to identify suspicious network activity, such as unusual login locations, and automates responses, including account suspension. Machine learning detects fraud patterns in real-time, reducing financial losses by up to 30% in some cases.

Healthcare – Protected Patient Data
Healthcare absorbs the second-highest data volume. Over 2.5 billion patient records globally, making it a hotspot for breaches, with an average cost of $10.1 million per incident. Artificial Intelligence in Zero Trust security, integrated in a custom AI developed solution, proactively acts as a vigilant guard who identifies access, safeguards sensitive data, and ensures it complies with HIPAA.
- Zero Trust Approach: Encrypts patient data both at rest and in transit, grants access only after continuous validation of user credentials and device compliance, and utilizes micro-segmentation to isolate medical devices and EHR systems.
- AI Enhancement: AI in zero-trust security monitors network traffic and user behavior, detecting anomalies like unusual data downloads. It automates responses, restricting access to compromised devices within seconds. This overall reduces the chances of breach risk in healthcare.
Retail – Secure Transactions
Retail faces significant risks from e-commerce fraud and point-of-sale (POS) breaches, with global retail fraud losses estimated at $40 billion annually. Zero Trust security safeguards platforms by verifying every device, user, and POS system, restricting employee access to sensitive customer data, and securing payment gateways to prevent network-wide compromises.
- Zero Trust Approach: Enforces device authentication, limits access to credit card data, and segments payment systems to contain breaches.
- AI Enhancement: AI blocks fraudulent transactions in real-time, using machine learning to identify patterns and alert on deviations, such as account takeovers. AI-driven systems reduce fraud by up to during peak shopping seasons.
Good Source – AI in eCommerce – Comprehensive Guide to Scale Your Business.
Manufacturing – Safeguarded Operations
Manufacturing is vulnerable due to an interconnected chain of devices and supply chains. With over 31% of manufacturers reporting cyberattacks in 2024. These attacks disrupt the production cycle and steal intellectual property, costing an average of $4.8 million per incident.
- Zero Trust Approach: Authenticates every device, enforces strict access controls for supply chain partners, and segments operational technology (OT) from IT networks to limit the spread of attacks.
- AI Enhancement: AI monitors behavior, detecting anomalies such as unusual sensor data, and automates the containment of compromised devices. Machine learning predicts supply chain vulnerabilities, reducing downtime by 15% and enhancing operational resilience.
- Problem-Solving: AI-driven Zero Trust isolates threats before they disrupt production lines, ensuring compliance with standards and protecting proprietary designs.
Government – Secure Public Systems
Government agencies manage sensitive citizen data and critical infrastructure, facing over 2.6 billion cyberattack attempts annually. Breaches threaten national security and public trust, with costs averaging $2.7 million per incident in the public sector.
- Zero Trust Approach: Enforces continuous monitoring of all access to public databases, requires ongoing user and device validation, and encrypts citizen data to prevent leaks. Secure remote access policies protect distributed government workforces.
- AI Enhancement: AI analyzes network traffic and external threat feeds to detect advanced persistent threats in real-time. Machine learning flags abnormal access patterns, unauthorized database queries, and automates system isolation, reducing response times by 40%.
- Problem-Solving: AI-enhanced Zero Trust ensures the rapid detection and containment of sophisticated attacks, thereby maintaining public trust and compliance with mandates such as CISA’s Zero Trust Architecture guidelines.
4 Top Reasons Your Organization Needs Zero Trust Security
The reason is clear: modern problems require modern and more advanced solutions. Though it’s not an overnight process. But small steps can make a huge difference.
Here are a few reasons to reconsider the adoption of zero-trust security.
1. Secure Remote and Hybrid Work
With the flexibility of access or work from ‘anywhere’, remote working teams are in every nook and corner. Be it coffee shops, airports, home, or anywhere else. The traditional network perimeters are gone. Zero trust ensures that every user and device is scanned and verified before accessing resources, regardless of location. AI-driven tools, such as adaptive authentication, scrutinize user behavior and device health in real-time. This keeps the entire ecosystem secure without slowing down.
2. Protect Against Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are on the rise, with costs averaging $4.5 million per incident. Zero Trust’s “never trust, always verify” framework leverages AI to flag abnormalities, constrain lateral movement, and apply least-privilege access, thereby preventing adversaries from making progress. Microsegmentation siloed important systems, constraining the blast radius of the breaches.
3. Streamline Cloud Migration
Shifting to the cloud? Zero Trust protects apps and data on-prem, cloud, and hybrid environments. AI-powered solutions, such as Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), deliver fine-grained control and real-time visibility, enabling secure access to cloud resources without compromising your network.
Also Read – Dive into the future of cloud computing – key trends and predictions.
4. Boost Compliance and Trust
Regulations such as GDPR and the EU AI Act require rigorous data protection. Zero Trust’s ongoing verification and AI-based compliance monitoring guarantee that you comply with industry standards. Securing sensitive information and restricting access helps you establish trust with customers and prevent expensive fines.
AI-integrated Zero Trust Security Implementation Plan for Business
Innovation strengthened by resilience tends to sustain itself longer and be more streamlined. For enterprises and large-scale businesses, every industry should operate with a proactive cybersecurity force. With breaches almost around the corner, an adaptive security posture, including the special forces of zero-trust’s protective layers, is essential.
You don’t have to overhaul the entire process or bundle up too many tools; all you need is a robust enterprise IT security solution that can help you achieve precise and accurate goals. However, we also have a generic plan defined to help you with AI in zero-trust adaptation.
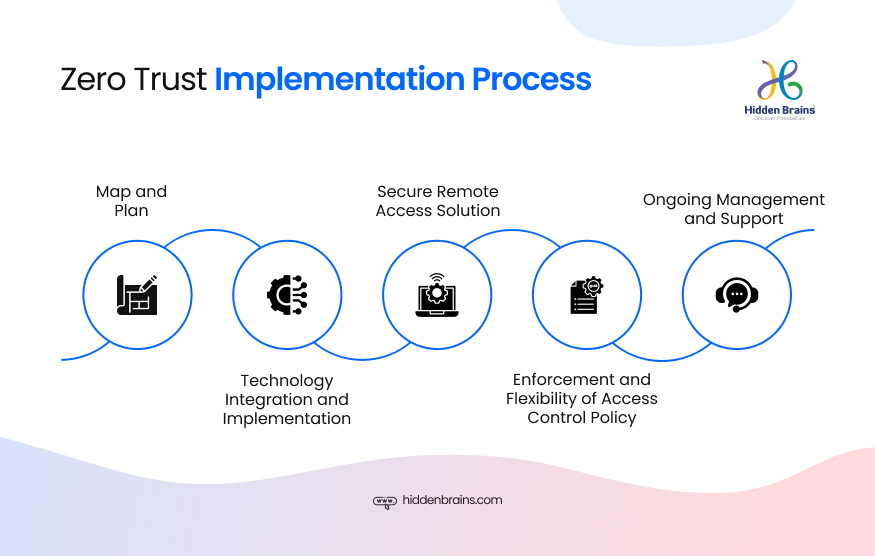
Phase 1: Assess and Plan
Before diving in, it’s time to introspect and lay the foundation of AI-driven zero-trust security.
- Map your assets – identifying critical data, applications, AI workloads, and devices. Identify what needs protection and any bottlenecks that may exist throughout the process.
- Audit existing security – Review your identity management, vulnerabilities, user behaviour, network access, and monitoring tools. Identify the gaps where AI and zero security can outpace with a proactive approach.
- Set Goals – Get a consultation to discover the exact blueprint for meeting your goals, such as faster threat detection, automated response, or secure innovation.
- Choose AI tools – Select AI-powered solutions such as UEBA (User and Entity Behavior Analytics), SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), or adaptive authentication that align with Zero Trust’s “never trust, always verify” mantra.
This audit and inventory of assets and vulnerabilities would help you make clear plans. If you’re unsure about the next step, be sure to consult with a cybersecurity expert.
Phase 2: Technology Integration and Implementation
Our cybersecurity experts will help you methodically build the pillars of a zero-trust architecture, assessing your environment. Understanding the inventory of assets, we can optimize, centralize, and automate the security network, ensuring tight security and more robust, better safeguarded solutions.
- Choose Zero Trust Tech – Get an audit and consulting from an expert who can help you with an AI-integrated solution, such as Secure Access Service Edge, for secure connectivity and Privileged Access Management (PAM) to prevent and control sensitive access.
- Secure AI Workloads – Leveraging methodologies and practices, use microsegmentation and encryption to protect AI models and data with AI-driven anomaly detection.
- Streamline with Experts – Cybersecurity experts would help you deploy and integrate these technologies seamlessly. Understanding your infrastructure can help you build a roadmap and deployment of best-fit solutions for your business.
Collaboration with experts ensures that we simplify and progress a zero-trust journey with an actionable roadmap catered to your business. Leveraging a set of principles, maturity, and capability of frameworks, we help you build potent security throughout the domain.
Phase 3: Secure Remote Access Solutions
Provide secure, controlled access to resources anywhere with AI-powered Zero Trust.
- Use Secure Access: Roll out AI-based solutions such as Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) to authenticate users and devices prior to access, regardless of location.
- AI for Risk Evaluation: Utilize AI to evaluate device health, user behavior, and risk levels in real-time, ensuring only trusted entities connect.
- Support Remote Work: Provide secure access to on-prem and cloud resources for hybrid teams, with Hidden Brains’ expertise in remote access solutions.
- Protect Against AI Threats: Include Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to prevent sensitive data leakage to external AI tools.
Phase 4: Enforcement and Flexibility of Access Control Policy
Build intelligent, adaptive policies that respond to risks and protect your business.
- Develop Dynamic Policies: Utilize AI to create access control policies that adapt to current risk factors, such as user activity or threat levels.
- Enforce Least Privilege: Limit users and AI systems to seeing only what they require, minimizing breach vulnerabilities.
- Automate Policy Updates: Utilize AI to monitor threats and automatically update policies, staying ahead of attacks with policy management support from Hidden Brains.
- Train Your Team: Train employees on new access policies and threat awareness through AI.
- Action: Collaborate with Hidden Brains to deploy AI-powered policy engines. Roll out a rapid training program on policy compliance.
Phase 5: Ongoing Management and Support
Stay ahead of your Zero Trust configuration with ongoing maintenance and AI-driven insights.
- Maintain Continuously: Leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) based on AI to monitor network traffic and identify threats in real-time.
- Proactive Upgrade: Update AI models and Zero Trust software repeatedly to address new threats, with Hidden Brains’ constant support.
- Scale Securely: Grow AI applications (e.g., fraud discovery or customer care automation) with Zero Trust guardrails.
- Stay Compliant: Utilize AI for regulatory compliance, such as the GDPR or the EU AI Act, to strengthen stakeholder trust.
Modernizing security requires a deliberate strategy and robust actions around the key pillars or core functioning of it. At Hidden Brains, we proactively undertake measures and build a modern security approach that is based on least-privilege access. Instead of risking the entire network, opt for a preventive solution that facilitates the prevention, detection, and mitigation of threats, allowing you to build brand trust and deliver your innovation.
Thrive in the era of tech led with a human approach ahead. Get a comprehensive solution to protect and build the empires of your enterprises.
FAQs
AI in zero-trust security is booming. It’s the next frontier. And in the checklists of most of the enterprises. However, if you are still undecided and would like to address a few queries, our FAQ has got you covered. Get answers to all your questions from our experts.
What is the function of Artificial Intelligence in Zero Trust architecture?
AI enables continuous detection, dynamic access controls, and real-time responses to threats, making Zero Trust frameworks more dynamic and robust.
How does AI-driven network security function?
AI inspects network traffic, identifies anomalies, and acts autonomously against threats, eliminating response time and labor for security operations.
What is AI-powered Zero Trust technology?
AI-powered Zero Trust technologies implement least-privileged access with AI, automate the verification of identity (such as biometrics), and dynamically adjust security policies based on user actions and network behavior.
How is machine learning advancing cybersecurity?
Machine learning identifies patterns, detects emerging threats, and adapts to evolving attack techniques, thereby minimizing false positives and enhancing threat prediction.
What is intelligent threat detection?
AI systems continuously scan for known and unknown threats, employing predictive analytics and real-time information to detect and react to attacks before harm is done.
In a Nutshell
As attackers become more sophisticated, ransomware groups proliferate, and advanced technology reveals new vulnerabilities, organizations opt for a trust-based security model. Implementing zero-trust security in your existing infrastructure may seem overwhelming, but it is not. Taking phased approaches and focusing on quick wins, you can reduce some of the complexity and risk associated with them. AI in zero-trust security not only enhances posture but also proves to be a valuable investment for addressing the most pressing business needs.





































































































![Sales & Distribution [Oil & Gas] Sales & Distribution [Oil & Gas]](https://www.hiddenbrains.com/blog/wp-content/themes/blankslate/assets/images/sales_and_distribution-icon.74d08193.svg)

![Fluid Terminal Management [Oil & Gas] Fluid Terminal Management [Oil & Gas]](https://www.hiddenbrains.com/blog/wp-content/themes/blankslate/assets/images/fluid_terminal_management-icon.4b3a27a4.svg)































![Sales & Distribution [Oil & Gas] Sales & Distribution [Oil & Gas]](https://www.hiddenbrains.com/blog/wp-content/themes/blankslate/assets/images/sales_and_distribution-icon.74d08193.svg?1.0.0)
![Fluid Terminal Management [Oil & Gas] Fluid Terminal Management [Oil & Gas]](https://www.hiddenbrains.com/blog/wp-content/themes/blankslate/assets/images/fluid_terminal_management-icon.4b3a27a4.svg?1.0.0)